Hyper Alarm Server vs. AlarmWorX64 Server
Hyper Alarm Server is an upgrade to the existing AlarmWorX™64 Server and provides improvements that overcome significant limitations in the existing AlarmWorX64 server. The following table summarizes some notable differences.
|
Feature |
AlarmWorX64 Server |
Hyper Alarm Server |
|---|---|---|
|
Alarm Source Areas1 |
X |
X |
|
Alarm Types 1 |
|
X |
|
Alarm Templates 2 |
X |
|
|
Customizable alarm logic |
|
X |
|
Integrated with AssetWorX™ |
|
X |
|
ISA 18.2 compliant |
X |
X |
|
Historical and third-party data inputs |
|
X |
|
Maximum related values per alarm |
20 |
Unlimited |
|
Multiple configurations in one database 3 |
X |
(need AssetWorX™ integration) |
|
Real-time data inputs 4 |
X |
X |
| Runtime configuration changes via DA points |
X |
|
|
Supports Heartbeat monitoring 5 |
|
X |
|
1 Alarm sources, also known as tags or data points, are used monitor alarm events or conditions. AlarmWorX64 configures alarm tags first, then associates one or more properties in the Areas section. Hyper Alarm Server uses alarm types to define alarm behaviors and conditions first, then associates the alarm source (properties) in the Areas section. See Alarm Configuration Differences.
2 AlarmWorX64 Templates use a set of alarm rules and conditions to cover all possible alarm scenarios. Hyper Alarm Server uses alarm types to configure alarm behavior that gets associated to specific properties types in the Areas section. See Alarm Configuration Differences. 3 Hyper Alarm Server uses one configurable database. When AlarmWorX64 gets integrated with Hyper Alarm Server, the same functionality asAlarmWorX64 gets achieved using equipment classes. The Bulk Asset Configurator is used to configure Hyper Alarm Server through AssetWorX. The ConverWorX™ utility can import AlarmWorX server database toHyper Alarm Server. 4 AlarmWorX64 accepts only real-time data inputs. (Undefined variable: Primary.Alarm Server) accepts real-time and historical inputs from Hyper Historian™ and third-party client data. 5 Hyper Alarm Server uses Heartbeat for monitoring server redundancy. Heartbeat monitors and detects data point activity, allowing the server to stop and start when needed. |
||
Alarm Configuration Differences
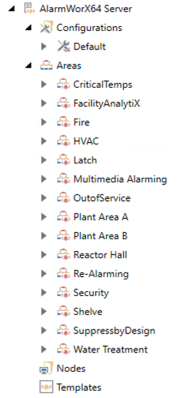
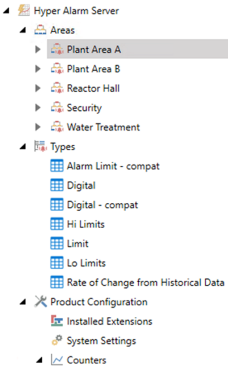
Alarms messages generated in the AlarmWorX™64 Server and Hyper Alarm Server use a ![]() hierarchical tree structure arranged by areas for creating and configuring alarms.
hierarchical tree structure arranged by areas for creating and configuring alarms.
To configure a single alarm in AlarmWorX64 Server, you create a Configuration entity and then configure the alarm (tag) underneath the defined configuration. The alarm source tag must be associated with one or more properties in the Areas section and related to the network via specified Nodes. The Areas list includes all possible configuration options and combinations of alarm types. With hard-coded alarm types, creating a multi-level alarm with more than two levels on each side of a normal condition (low or high) is not possible. The AlarmWorX64 configuration process is considered complex and not intuitive—this led to the introduction of alarm templates with preset alarm source properties, rules, and conditions to reduce the need to configure each alarm source repeatedly.
Hyper Alarm Server uses a different concept to configure alarms. Instead of creating a complex alarm source configuration that covers all possible scenarios and then using templates, you configure the specific properties in Alarms and associate them (as tags) with the defined alarm Types to define an alarm behavior and structure. This concept allows users to design alarms based on their project needs without templates.
What's Next ?